Atmosphere and Characteristics
How does weather differ from climate?
Weather is constantly changing and refers to the state of the atmosphere at any given place and time
Climate is based on long term weather observations and help describe a region or place.
2. Describe the composition of the atmosphere including majot components and variable components
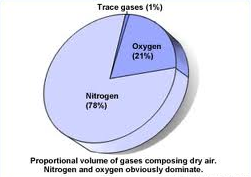
** Air is not actually a specific gas or element but instead is a “mixture” of gases
99 % of clean, dry air is composed of nitrogen and oxygen
Major components:
- Nitrogen
- Oxygen
- Argon 0.93 %
- Carbon dioxide 0.039 %
Variable components vary from time to time and place to place. They include water vapor, dust particles, and ozone.
Water vapor is the source of all clouds and precipitation. It absorbs the most solar radiation.
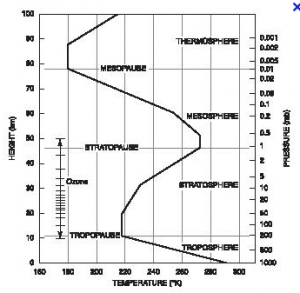
What are the four vertical layers into which the atmosphere can be divided by temperature?
- Thermosphere contains only a fraction of the atmosphere’s mass. Temp increases b/c oxygen and nitrogen absorb high-energy solar radiatipon
- Mesosphere temperature decreases w/ altitude
- Stratosphere ozone is located here. The ozone collects UV light which heats the stratosphere
- Troposphere weather occurs here temperature decreases w/ altitude
The atmosphere “thins” as you travel away from Earth until there are too few gas molecules to detect. This causes a decrease in air pressure as altitude increases.
—————————————————————————————————
Heating and the Atmosphere
Objectives:
How are heat and temperature related?
- Heat is the energy transferred from one object to another beacuse of a difference in their temperatures.
- Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of individual molecules or atoms in a substance.
What are the three major mechanisms of heat transfer?
Conduction The transfer of heat through matter by molecular activity. The energy of the molecules is transferred by collisions from one molecule to another.
Convection is the transfer of heat by mass movement or circulation within a substance. It occurs in fluids like the air and in the oceans. It can also occur in solids like the Earth’s interior over time.
Radiation travels out in all directions from the source and can travel through the vacuum of space as it requires no medium. Solar radiation reaches Earth by radiation.
There are four laws governing radiation
- All objects, at any temperature, emit radiant energy
- Hotter objects emit more total energy per unit area than colder objects
- The hottest radiating bodies produce the shortest lengths of maximum radiation
- Objects that are good absorbers of radiation are good emitters as well.
How is the atmosphere affected by each of the three heat transfer methods?
When radiation strikes an object, there are usually three different results:
- Some energy is absorbed and converted into heat raising the temperature of the object
- Transparent substances such as air and water vapor transmit the energy resulting in no energy change
- Some energy may reflect (bounce off) the object without being absorbed or transmitted.
Know picture page 486
Reflection verses scattering
In reflection, the electromagnetic radiation “bounces” off an object with the same intensity that it strikes the object.
In scattering, many weaker waves are dispersed in different directions. Scattering explains why a room is sunlight even if it does not have direct access to a window.
Temperature Controls
Objectives:
What is a temperature control?
Any factor that causes temperature to vary from time to time and place to place
- latitude
- heating of land and water
- altitude
- geographic position
- cloud cover
- ocean currents
Know graphs pages 489-492
How do the heating of land and water differ?
Water heats more slowly than land but also cools more slowly than land. Water moderates the temperature.
Why do some clouds reflect a portion of sunlight back to space?
Albedo is the fraction of total radiation that is reflected by any surface
Many clouds have a high albedo, and therefore reflect a significant portion of sunlight that strikes them back to space.