Time to Think
Feb 1 Mon
No opener- new unit!
Feb 2
Snow day!
Feb 3
More snow!
Feb 4 Thurs
Construct a family tree with the phenotypes and genotypes for each member.
A brown-eyed couple had three children: two blue-eyed boys, and the youngest was a girl with brown eyes. Their youngest daughter marries a brown-eyed man and they had three daughters, two blue-eyed daughters and one brown-eyed.
Feb 5 Fri
——————————————————————————————————————-
Jan 25 Mon
For each group of words, identify the one word that is LEAST like the others and explain why you chose that word.
- Homozygous Tt Purebred TT
- Hybrid Heterozygous tt Tt
- Probable ratio Actual ratio Punnett Square
- Long haired cat hh Physical characteristics Traits
Jan 26 Tues
Jan 27 Wed
Jan 28 Thurs
Jan 29 Fri
———————————————————————————————-
Jan 18 Mon
No School
Jan 19 Tues
Chapter 10.3 Stem cells
Stem cell case study work in groups to solve case
Jan 20 Wed
Finish case study
Begin ch 11.1 and 11.2 Genetics (Probability)
Vocab for ch 11.1 and 11.2
Jan 21 Thurs
LAB Principles of Genetics
Jan 22 Fri
Monohybrid cross formative quiz
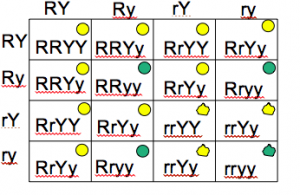
Phenotypic ratio:
- Rough and Yellow:
- Rough and green (white):
- Smooth and Yellow:
- Smooth and green (white):
—————————————————————————-
Jan 11 Mon
- What are 2 problems that cells encounter if they grow too large?
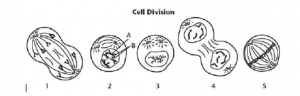
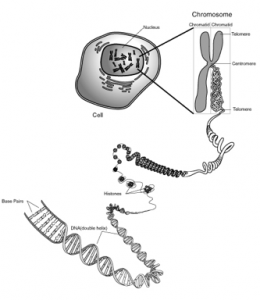
 2. Label the following in the diagram: chromosome, sister chromatids, and centromere
2. Label the following in the diagram: chromosome, sister chromatids, and centromere
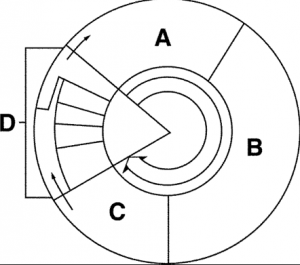
3. What are the 5 stages of the cell cycle in order?
4. What letter(s) are included in interphase?
5. In what letter(s) does mitosis occur?
Jan 12 Tues
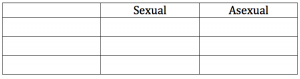
- Compare sexual and asexual reproduction by completing the table. Write your own categories in the left hand column.
From “The Cell Cycle Computer Lab,
2. What cyclins increased the rate of cellular reproduction?
3. What cyclins decreased the rate of cellular reproduction?
Jan 13 Wed
- How is cancer uncontrolled cell growth?
- Is interphase part of mitosis? yes or no
- Identify each phase of the cell cycle.
Jan 14 Thurs
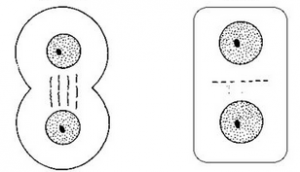 Which cell is the plant cell and which cell is the animal cell?
Which cell is the plant cell and which cell is the animal cell?
How does cytokinesis differ between plant cells and animal cells?
What is the “spindle”? What is its function?
Jan 15 Fri
No opener- Quiz
_________________________________________________________
Jan 7 Thurs
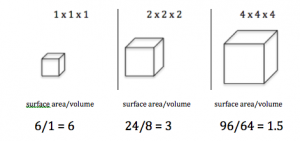
- An elephant is larger than a mouse. Do elephants have larger cells than mice?
2. If a cell doubles in size, what happens to the surface area to volume ratio?
3. What is a problem with a low surface area/volume ratio?
March 2
- DNA is a polymer of ______________ which are composed of _________, ___________, and a ______.
- Which two nitrogen bases are purines?
- Which two nitrogen bases are pyrimidines?
- Why do the bases join with one purine and one pyrimidine instead of either two purines or two pyrimidines?
Jan 8 Fri
No opener Computer Lab
March 3 Tues
- What composes the sides of the DNA ladder?
- What composes the “steps’ of the DNA ladder?
- What kind of bonds hold the steps of the ladder together?
March 4 Wed
March 5 Thurs
- Quiz Chapter 12
- Structure of DNA + DNA replication
March 6
————————————————————————-
Feb 23 Mon
Feb 24 Tues
No opener Quiz
Feb 25 Wed
Feb 26 Thurs
- What happened in the Griffith experiment (with the mice) when he mixed the R-strain (harmless) with the heat-killed S-strain (harmful)? What is this process called?
- What molecule stores and codes information in a cell?
- In the Hershey-Chase experiment, what happened to the bacteria that had been infected by viruses that had radioactive DNA?
- What happened to the bacteria that had been infected with viruses that had been marked with radioactive proteins?
Feb 27 Fri
- A nucleotide is the basic unit of DNA. What three molecules make up a nucleotide?
- What are the four nitrogenous bases?
- Complete the chart by matching each nitrogen base to its compliment.
A–> _____
G–> _____
T–> _____
C–> _____
————————————————————————————————
Feb 16 Mon
- List the steps of meiosis in order
- What are two ways mitosis and meiosis and differ?
- What process is used to repair a broken arm?
- What process is used to make gametes?
Feb 17 Tues
- Why must gametes be haploid?
- How does crossing over increase genetic diversity?
- What is a tetrad?
Feb 18 Wed
Construct a T chart with Mitosis as one heading and Meiosis as the other heading. Place the terms in the appropriate column.
Feb 19 Thurs
1. What is…
- monosomy
- trisomy
- deletion
- addition
2. Consider meiosis. In which steps could mistakes (mutations) occur that would affect the gametes?
Feb 20 Fri
- What is a karyotype?
- How are karyotypes made?
————————————————————————————-
Feb 9 Mon
C is dominant to cch, cch is dominant to ch, ch is dominant to c.
1. Cross a Cc rabbit with a cchch What are the phenotypes of the offspring?
2. A chinchilla coated rabbit (cch) and a Himalayan (ch) have 25% albino offspring. What is the genotype of the parents? What are the genotypes for the rest of the offspring? (Do a single factor cross)
3. In Pigs, curly tails (C) are dominant to straight tails (c). Pink (P) is dominant to gray (p).
ccPp, Is this an example of multiple alleles? If not what is?
Feb 10 Tues
Help! There has been a mix up in the hospital. Use your knowledge of genetic to help match the baby back to the correct family.
- Mr. and Mrs. Jones both have blood type A.
- Mr. and Mrs. Smith both have blood type AB
- Mr. and Mrs. Clark both have blood type B. The Clark’s oldest child is blood type O.
- Mr. Pearson is blood type O while Mrs. Pearson is blood type A.
** Mrs. Jone’s parents both have type AB blood.
Baby # 1 type A blood belongs to the ___________________ family.
Baby # 2 type B blood belongs to the ___________________ family.
Baby # 3 type AB blood belongs to the ___________________ family.
Baby # 4 type O blood belongs to the ___________________ family.
Feb 11 Wed
- No opener quiz
Feb 12 Thurs
- Review. List the stage of the cell cycle in order.
- Identify each phase of the cell cycle.
Feb 13 Fri
Write directions on the back of your blue sheet.
- Cut and paste the order of meiosis (I-P-M-A-T-P-M-A-T)
- Label where meiosis I and where meiosis II begins.
- Cut and paste the explanation of each phase of meiosis, label each phase (ex. Prophase I, Metaphase I)
- Label the spindle fibers, homologous chromosomes, and centrioles.
- Label where the cells are haploid or diploid. (n or 2n)
——————————————————————————————-
Feb 2 Mon
No opener– snow day!
Feb 3
No opener- going over quizzes
Feb 4 Wed
No opener– Snow day!
Feb 5 Thurs
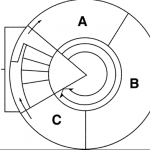
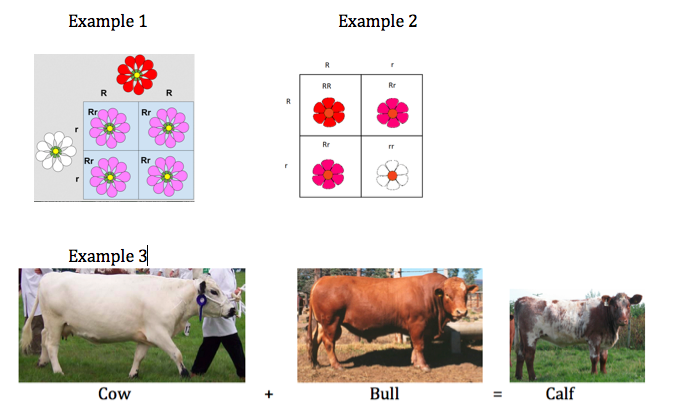
Use the images to identify each type of inheritance.
A. Mendel’s principle of dominance B. Co-dominance C. Incomplete dominance
————————————————————————————–
Jan 26 Mon
Examine the following terms and choose the term that is least like the others. Be able to justify your choice.
- Heterozygous Purebred Hybrid Hh
- RR rr Homozygous Hybrid
Jan 27 Tues
In Guinea pigs, Rosette is dominant to smooth
Short hair is dominant to long hair.
What are the 4 possible phenotypes for a cross between these two traits (rosette or smooth and short or long hair)
Jan 28 Wed
Part 1
1. Construct a pedigree using the following information.
- The grandparents of two boys are in generation I.
- They have 3 girls and 1 boy. (oldest to youngest)
- The oldest daughter marries and has two sons.
Part 2
2. Use the following information to write the genotypes and phenotypes for each person in the pedigree
- “N” is normal to “n” represents a disease
- II-3 and III-1 have the disease
Jan 29 Thurs
Jan 30 Fri
No opener Quiz ch 11.1 and 11.2
———————————————————————-
Jan 19 Mon
No School
Jan 20 Tues
Opener Vocabulary
- Homozygous Having two identical alleles for the same trait
- Heterozygous Having two different alleles for the same trait
- Genotype genetic make up of an organism or the alleles that the organism carries
- Phenotype the physical characteristics of an organism
In cats, long hair is recessive to short hair.
Cat A
What is the phenotype of Cat A? The genotype of Cat A?
What is the phenotype of Cat B?
Why don’t we know the genotype of Cat B?
What would you need to know in order to determine the genotype?
Jan 21 Wed
In Icelandic sheep, polled (no horns) are dominant to horned.
- Write the genotype(s) for a polled sheep
- Write the genotype(s) for a horned sheep
- Why are there two possibilities for polled sheep but only one possibility for horned sheep?
- Draw a Punnet square for a cross between a homozygous polled sheep and a heterozygous polled sheep. What are the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the offspring?
- Draw a Punnet square for a cross between a horned sheep and a heterozygous polled sheep. What are the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the offspring?
Jan 22 Thurs
Opener was a short formative quiz.
Jan 23 Fri
- What is the probability of tossing a coin and it landing on heads?
- When tossing a coin 3 times what is the probability they will all land on heads?
- I crossed two heterozygous short haired cats and I got half short haired and half long haired. Explain what happened.
———————————————————————————————-
Jan 12 Mon
Computer lab-
- register for QuizStar
- register for on-line text
- Complete reading guide ch 10.1/10.2
- take ch 10.1/10.2 practice quiz
- Homework: The Cell Cycle check yourself
Jan 13 Tues
Describe the structure of a chromosome
Why is DNA “packaged” into tightly bundled chromosomes?
Jan 14 Wed
- No opener- Quiz ch 10.1/10.2
Jan 15 Thurs
How do cells become specialized for different functions?
What are stem cells?
What are possible benefits and issues associated with stem cells research?
Jan 16 Fri
1. What protein helps regulate the cell cycle?
2. An unspecialized cell that does not have a specific job yet is called?
3. What are two examples of an unspecialized cell?
————————————————————————————————–
Jan 5 Mon
No Opener- First day of term
Jan 6 Tues
- An elephant is larger than a mouse. Do elephants have larger cells than mice? Explain your answer.
- If a cell doubles in size, what happens to the surface area to volume ratio?
- What are 2 problems that cells encounter if they grow too large?
- What is the test retake policy?
- True or False: Cell phones or other electronic devices can be used during class while working independently
- True or False: It is OK to modify directions for a lab if you see a more efficient way to perform it
Jan 7 (Wed)
What are the 5 stages of the cell cycle in order?
What letter(s) are included in interphase?
In what letter(s) does mitosis occur?
Compare sexual and asexual reproduction by completing the table. Write your own categories in the left hand column.
Jan 8 (Thurs)
1. Label the following in the diagram: chromosome, sister chromatids, and centromere
2. Identify each phase of the cell cycle.
Jan 9 (Fri)
No opener — Lab day.
There will be a check of your unit packet on Monday. You are responsible for finishing the following:
- Class notes
- Computer Lab: The Cell Cycle
- Lab: (Jello block) To determine which is more efficient for transport through the cell membrane
- LAB: Determining the time needed for mitosis
————————————————————————————————
April 1 Tues
Natural selection requires
1. More individuals than can survive
2. Variation in the population
3. Variable Fitness
Same structure + Different Selective Pressure = Descent with modification
Jan 28 Tues
In aliens, patterned bodies are dominant to white bodies and wings are dominant to no wings. Write the genotype of each alien in the sketch.
Why does the alien on the left have more than more possible genotype but the alien on the right only has one?
Find the genotypes of the parents for the following scenarios:
Orange is dominant to white in tigers.
- What is the genotype of a heterozygous male?
- What color is he?
- What is the genotype of a homozygous orange female?
- What is the genotype of a white tiger?
In a certain species of monster, fur (F) is dominant to no fur (f) and spikes (S) are dominant to no spikes (s).
- What is the genotype of a heterozygous furry monster without spikes.
- What is the genotype of a homozygous furry monster who is heterozygous for spikes?
- What is the genotype of a furry monster with spikes who has a baby with neither fur nor spikes?
Unit 1 Week 1
Jan 6 (Mon)
An elephant is larger than a mouse. Do elephants have larger cells than mice? Explain your answer.
If a cell doubles in size, what happens to the surface area to volume ratio?
Jan 7 (Tues)
What is the test retake policy?
When is it appropriate to wear goggles?
Jan 8 (Wed)
No opener, computer lab
Jan 9 (Thurs)
Identify the phases of the cell cycle from the power point
Jan 10 (Fri)
—————————————————————————————-
Jan 13 (Mon)
Be able to identify the various stage of the cell cycle in prepared onion root tip slides
Jan 14 (Tues)
Jan 15 (Wed)
Ch 10 test
Jan 16 (Thurs)
Jan 17 (Fri)
———————————————————————————————————-
Jan 20 (Mon)
NO SCHOOL
Jan 21 (Tues)
Jan 22 (Wed)
Look at pictures.
- What traits are heritable? What traits are man made?
- Why are there so many different types of dogs? Do these dogs share the same DNA?
Jan 22 (Thurs)
- Why do organisms resemble their parents?
- Why are you different from your parents and siblings
- What does it mean for a trait to be dominant? Recessive?
Jan 23 (Fri)
Circle the term that does not match the other terms.
1. blue eyes heterozygous bb recessive
2. phenotype blue eyes Bb physical characteristics
————————————————————————————————————
Aug 20 (Tues)
In an experiment, a researcher is trying to determine if Sparkle toothpaste whitens teeth better than the regular brand. The researcher records the shade of the subject’s teeth before and after the subjects have used Sparkle for one month.
- What is the independent variable?
- What is dependent variable?
- Which group is the control group?
- Which group is the experimental group?
Aug 21 (Wed)
Distinguish between a scientific law, a theory, and a hypothesis.
- How does a law differ from a theory and a hypothesis?
- How does a theory differ from a law?
Aug 22 (Thurs)
- Which sense, sight or taste is stronger in humans?
- How does that help humans survive?
Aug 23 (Fri)
Quiz – no opener
————————————————————————————————————————————————
Aug 26 (Mon)
Aug 27 (Tues)
Aug 28 (Wed)
Aug 29 (Thurs)
Aug 30 (Fri)