Chapter 9.1 Cellular Respiration: An overview
Objectives:
- Where do organisms get energy?
- What is cellular respiration?
- What is the relationship between photosynthesis and respiration?
Organisms get the energy they need from food. Food molecules contain chemical energy in their bonds which is released when those bonds are broken.
What organelle converts the chemical energy in food into a form of energy that is useable to the cell?
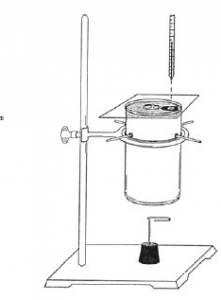
Energy is measured in calories or the amount of energy needed to raise 1 gram of water 1 degrees celcius.
Here is a simple calorimeter made from a pop can.
Pathways to obtain ATP from glucose
Respiration and photosynthesis are opposite processes:
Respiration: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 –> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O
Photosynthesis: 6 CO2 + 6 H2O –> C6H12O6 + 6 O2
What the reactants of respiration? photosynthesis?
What the products of respiration? photosynthesis?
Review videos:
The Penguin Prof
mhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aA8d-tt6dII
mhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=00jbG_cfGuQ
Khan Academy:
mhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2f7YwCtHcgk&list=PL17CED09ADECF2FDF&index=2
9.3 Fermentation
Energy and Exercise
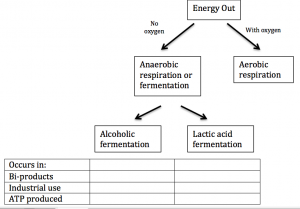
How do organisms obtain energy when oxygen is NOT available?
Organisms can make ATP by glycolysis and fermentation
Alcoholic fermentation occurs in yeast and few other microorganisms
Pyruvic acids + NADH –> Alcohol + carbon dioxide + NAD+
Lactic acid fermentation occurs in most organisms
Pyruvic acid + NADH –> Lactic acid + NAD+
This process is important to the food industry as prokaryotes are used to make a variety of foods and drinks.
pickles, sauerkraut, and kimchi are produced using lactic acid fermentation